Building Pensions SuperTeams
“If you want to go fast, go alone.
If you want to go far, go together.”
– African Proverb
Why we need six honest serving men to solve the pensions challenge
Thanks to Rudyard Kipling’s six honest serving men we have a mindset, toolset and skill set to understand and solve the challenges that face our pension funds.
Continue reading “Why we need six honest serving men to solve the pensions challenge”
Pensions – Two sets down, can we come back?
The enormity of Andy Murray’s win at Wimbledon last Sunday still hasn’t quite sunk in across our nation.
Continue reading “Pensions – Two sets down, can we come back?”
Staying Classy – Sharing Ideas and Repairing Pensions Deficits
Last week, we at Redington released an annual publication called Asset Class 2013. It was put together by Redington Head of IC David Bennett and his team of consultants, who deal with over £270 bn of assets and the people who run those assets, on a daily basis, helping them to repair deficits and improve member security through smart investment strategy.
Continue reading “Staying Classy – Sharing Ideas and Repairing Pensions Deficits”
Are you SMART? How pension funds can set the right kinds of goals.
Pension funds face an eternally difficult process of setting goals and then making sure they reach them. It doesn’t sound complicated, but it is.
Continue reading “Are you SMART? How pension funds can set the right kinds of goals.”
Pitching to solve the Pensions Crisis
Last Tuesday 21st May 2013 was KPI Pitch Fest the last part of the Daniel Priestly Key Person of Influence Course. The judges were led by the iconic Mike Harris, Daniel Priestly, James Paton-Philip from Pinsent Masons, Sally Preston Founder & Managing Director at The Kids Food Company ltd, Jenny Campbell CEO at YourCash and Steve Henry Co-founder at Decoded. Thank you for an incredible opportunity and a great evening. Well done to pitch fest winner – Liz Marsh and fellow runner-ups Hannah Foxley, Karen Bailey and Viv Grant and A Rafael Dos Santos. Below I have shared my pitch from pitch fest.
A game of Snakes and Ladders
In the UK, as a final salary pension fund, you may be feeling as if you have just landed on a ladder and risen several rows on the board game closer to the finish: full funding. The FTSE100 equity index had its best performing January since 1989 and the S&P500 has broken through 14,000. These are levels not reached since before the onset of the Global Financial Crisis in 2007. All of this is good news for pension funds invested in equities as their funding levels will have improved significantly over the past few months.
In the US, it appears that many pension funds have landed on a “snake”, as corporate after corporate announces significant cash injections to their underfunded pension funds. So much so that, when I made a comment on Twitter about Ford’s $5billion funding of its pension fund, it elicited the response from @blackbullion “isn’t Detroit an underfunded pension fund that makes some cars?” . Ford isn’t alone in making significant cash contributions to its pension funds. It is joined by other large US corporations Honeywell, Raytheon etc. All of whom have stepped on the proverbial pensions snake.
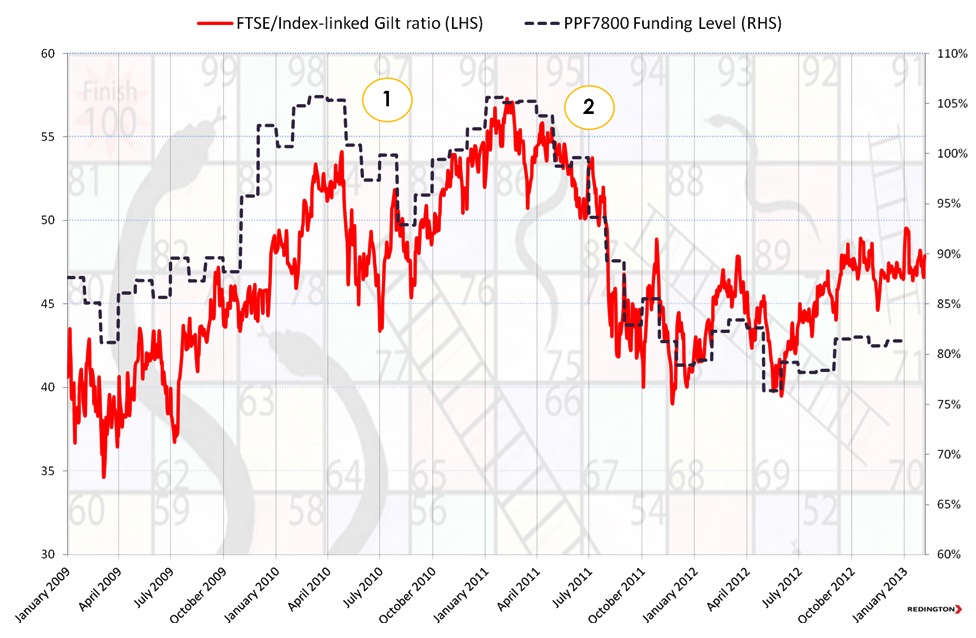
The big question is what should they do next? This highlights the difference between an “outcome focused investment strategy” or a “peers based investment strategy”. An outcome focused pension fund will have clear goals and objectives combined with regular monitoring of its assets, liabilities, funding level and perhaps its ongoing required rate of return. They will likely focus on risk and return and see the recent strong outperformance of equities over liabilities (see chart) as an opportunity to take-profit; that is, bank the outperformance of their assets over their liabilities. Within a peers based investment strategy, on the other hand, more focus is laid on the value of assets than on funding level.
The chart below shows the relative value of equities to index linked gilts plotted against the PPF 7800 funding ratio. The FTSE/Index-Linked Gilt ratio is calculated by taking the market level of the FTSE (6,000) divided by the price of the 2037 Index Linked Gilt (120). This gives a ratio of 50. The FTSE/Index-Linked Gilt ratio can be enlightening as a “rule of thumb” proxy for pension funds’ decisions to switch between equity and fixed income. Opportunities to dynamically “take profit” out of equities and into index linked gilts to hedge the liabilities are highlighted at the peaks (1) and (2). The PPF 7800 Funding Ratio is given in the background to provide context of the relative performance of a large sample of pension funds.
Chart showing the relative value of Equities (FTSE100) to Index Linked Gilts (ILG 2037) – plotted against the PPF7800 Index
 Source: Bloomberg, PPF and Redington
Source: Bloomberg, PPF and Redington
Checklist for “taking profit” and dynamic risk management
- Do you have clear goals and objectives?
- Do you have take profit triggers in place?
- Are they market yield based?
- or
- Funding level based?
- or
- Versus your “Flight Plan” and you “Required Rate of Return”?
- Do you have regular monitoring in place to capture these opportunities?
- Do you have the governance and delegation to be agile and take advantage of these opportunities?
Which is better? We are all faced with the same financial uncertainty. However, if you had the opportunity to remove the big snake on the final row to the finish in exchange for removing one ladder from the board – would you? My view is that repairing the deficit and improving the security of the pensioners through prudent and disciplined risk management is the best way forward.
Happy to discuss.
Goals 2013 – a year of Goals, Commitment and Accountability
Happy New Year! After a big night out we wake-up and write down our new year’s resolution(s). It’s the usual wish list lose weight, get fitter, earn more money, give-up drinking, smoking etc.
On Tuesday 1st January I listened to an excellent webinar by Shaa Wasmund “Why you should Forget New Year’s Resolutions”. @shaawasmund is the best selling author of “Stop Talking, Start Doing”, the UK’s best selling business book of 2012!
She told us that by the 19th January, less than 3 weeks in, 85% of these New Year’s resolutions fail, leaving us feeling like a failure. Part of the challenge is that New Year’s resolutions are more like a wish list with no focus or commitment to achieve them, and/or they are too large a goal to be realistically achieved.
Please read Shaa’s blog – 5 Ways To Make Your Resolutions Stick
In 2013 I wanted to share a different way of achieving your goals. Shaa suggests first we make a #Commitment – one clear goal with a focus on how to achieve it i.e. a plan of action to make it happen. Second we need to be #Accountable – share your commitment with a friend or colleague this accountability makes sure you stay on track and achieve your goals.
I learned this lesson in October 2012 when I did the 10,000 push-up challenge.
- Goal – 10,000 push-ups in one-month (325/day)
- Commitment (and discipline) to do a minimum of 250 every day and to aim for 325/day
- Accountability – I challenged my super fit colleague and ALM black-belt Dan Mikulskis @danmikulskis to the challenge and made myself accountable to my colleagues and clients.
Suffice to say we both achieved success and bigger pectoral muscles!
In 2013 think about one achievable goal, make a commitment and share it with a friend or colleague. Depending on the goal it takes about 66 days for something to become a habit e.g. 50-sits ups a day vs drink one glass of water a day.
And remember “we must all suffer from 1 of 2 pains: The pain of discipline or the pain of regret” – Jim Rohn.
My commitment for 2013 is to become an author to write my book “Take Control” and the 7 Step Framework for pension funds to achieve full funding.
Respect the training! Honour the commitment! Cherish the Results!
Whats your commitment to be better and smatter in 2013?
Good luck!
Rob
Step 1 – Preparation – Clearly written goals and objectives
The Pension Risk Management Framework “PRMF”
“If one does not know to which port one is sailing, no wind is favourable.”
– Seneca
Pension funds should start the process of taking control of their fund by defining the situation clearly and realistically, by setting clear goals and objectives that can be written down into a robust Pension Risk Management Framework “PRMF” document. First of all, the PRMF must clearly state the date that all parties agree full funding should be reached, for example, 2032. From there, a number of key factors can be identified and agreed.
The required rate of return needed from the assets as well as the necessary contributions to reach this date, for example Libor + 3.00%, must be calculated and included in the PRMF. Next, the framework clearly lays out the risk appetite of the trustees and the sponsor, so that all stakeholders understand each other’s goals and constraints. For example a pension fund might agree that their risk appetite is a 10% relative drop in funding level or a £100 million absolute drop in funding level in any one year. Next, the liquidity requirements needed to pay the pensioners and meet any potential collateral requirements are identified, measured, and laid out in the document. This is increasingly important since most pension funds in the UK are closed to future accrual which may result in (deficit) contributions being less than the pensions in payment. This situation is known as negative cashflow and introduces another risk which is the path dependency of the investment returns versus the liabilities. This requires the pension fund to think about assets that have greater income security year-on-year, for example credit, see steps 4 and 5. All assumptions, like the equity risk premium or the likelihood of mean reversion in bond yields, must be realistic rather than aspirational.
“The pessimist complains about the wind; the optimist expects it to change; the realist adjusts the sails.”
– William Ward
This PRMF document forms the operating system, a pension’s iTunes if you like, for any funding, investment and risk management decisions and actions. The PRMF allows the stakeholders to move away from a traditional asset based asset allocation framework to a risk based asset allocation framework; all key factors are considered simultaneously and, vitally, all decisions are completely informed. Without a well thought-out PRMF in place, pension funds are likely to struggle to generate the returns needed to meet their liabilities without running too much risk. In this period of economic and political uncertainty it is difficult to foresee what challenges and delays to the investment and funding plan lie ahead. It is therefore crucial to constantly be reminded of the fund’s goal, the fund’s PRMF.
In agreeing an effective PRMF, trustees and sponsors – in conjunction with their advisors – must be productively paranoid. The process necessarily leads them to ask questions like “How could this situation get worse?” “What if the Eurozone debt crisis deepens?” “What if this low growth environment in the UK and globally persists, and gilt yields start to resemble the Japanese curve?”. The stakeholders must be comfortable that solutions to these situations exist, and that the PRMF they are laying out is sufficiently inclusive to allow for effective action when the time calls.
With the PRMF in place, stakeholders are now able to make informed, effective and fast decisions. Continually readjusting the sails is the most important part of navigating towards a goal, and pension funds must be able to do this effectively; it sounds simple, but without all the goals, risks and constraints laid out in a PRMF document, pension funds have struggled to make decisions at all. The next step in this initial phase of preparation and planning is to agree and make clear responsibilities for making and carrying out decisions, setting hard deadlines for completion and review.
“I may say that this is the greatest factor — the way in which the expedition is equipped — the way in which every difficulty is foreseen, and precautions taken for meeting or avoiding it. Victory awaits him who has everything in order — luck, people call it. Defeat is certain for him who has neglected to take the necessary precautions in time; this is called bad luck.”
— from The South Pole, by Roald Amundsen
Finally, as we will see later on, in step 7 is to follow-up, monitor the decision, compare actual results with expected results, and then generate new solutions, new courses of action, and readjust the sails.
Unsurprisingly perhaps, clients who have implemented the PRMF and the 7 steps approach have been able to enhance their governance and achieve better results. Stating the goal and possible problems clearly significantly improves a pension plan’s governance structure by encouraging accountability, transparency and discipline between all key stakeholders. The framework, rather than constraining the pension fund, allows the stakeholders to be creative and develop many new solutions, as we will see later in the 7 steps, to meeting the goal of generating consistent and sustainable real returns to pay the pensioners and reach full funding. And it’s not just conjecture: research by Professor Gordon Clark from Oxford University shows that an enhanced governance framework can lead to a governance premium on investment returns, thereby materially improving the funding position of a fund.